Lectures
Naren Singh Rao’s lectures offer questioning perspectives on social, political, cultural and media issues.
-
by Abhai Singh Tanwar This blog explores the four major theories of the press based on the work authored by Fred Siebert, Theodore Peterson, and Wilbur Schramm. Journalism is known as the fourth pillar of democracy in India, but is it truly the case? You may agree and disagree with the ongoing state of the
-
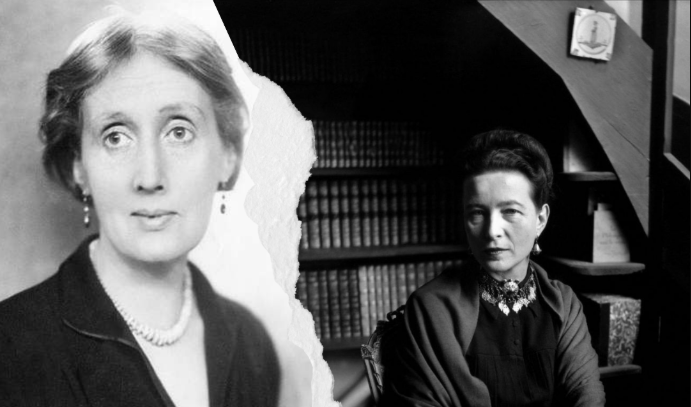

This essay explores how Virgina Woolf and Simone de Beauvoir reveal the structural barriers that silence women. Through Woolf’s “Shakespeare’s Sister” and de Beauvoir’s idea of woman as the ‘other,’ it critiques how patriarchy shapes both opportunity and identity even in the most ‘progressive’ spaces.
-

How do individuals come to identify with a nation of strangers? Drawing on Benedict Anderson’s theory of print capitalism, this essay examines how the rise of print media fostered shared language and collective consciousness, enabling people to imagine themselves as part of a unified national community.
-

The Culture Industry Theory, developed by Theodor Adorno and Max Horkheimer of the Frankfurt School, critiques the mass production of culture under capitalism. These thinkers, though rooted in Marxist ideology, became disillusioned with Marxism after witnessing the failure of revolutionary movements in Europe and the rise of fascism in Germany.
-

Cognitive Dissonance Theory, introduced by Leon Festinger in 1957, explains the psychological discomfort that arises when an individual holds contradictory beliefs, attitudes, or values, or when their behaviour clashes with what they truly believe. The term “cognitive”relates to the mind, and “dissonance” refers to a state of disturbance or inconsistency.
-
In today’s world, the intersection of politics, media, and ideology is more powerful than ever. From Marxist theories about class struggle to modern media effects theories, the way information is disseminated and consumed plays a pivotal role in shaping societal beliefs and actions. Let’s break down some key concepts that explore how power, culture, and…
-

Antonio Gramsci’s concept of cultural hegemony exposes how ruling classes maintain control by shaping culture and ideology, making their worldview seem natural. True revolution requires a “war of position”, that is, a cultural struggle to challenge the dominant beliefs and empower the masses to reclaim their voices.
-
The Propaganda Model by Herman and Chomsky unfolds how corporate media serves those in power through five filters: profit-driven ownership, advertiser funding, reliance on second-hand sources, flak, and bias. In India, this leads to pro-corporate narratives and suppression of dissent, weakening the media’s role as the fourth pillar of democracy.